Historically, the performance of the telecoms sector has been closely correlated with the performance of the wider economy, with reductions in GDP being accompanied by corresponding falls in operator revenues as incomes are squeezed. However, the nature of the current coronavirus crisis, and telecoms’ role in easing it, could mean a divergence from this trend. In particular, social distancing measures appear to be driving a significant increase in the usage of telecoms services. Even in the longer term, this might translate into a sustained rise in the demand for telecoms services as more people become comfortable with home working and other forms of remote interaction.
A downturn like no other?
The share prices of telecoms operators have, on average, broadly followed the stock market as a whole (as measured by the STOXX Europe 600) during the coronavirus outbreak, taking a hit of just under one fifth since the start of February – see the Figure below.
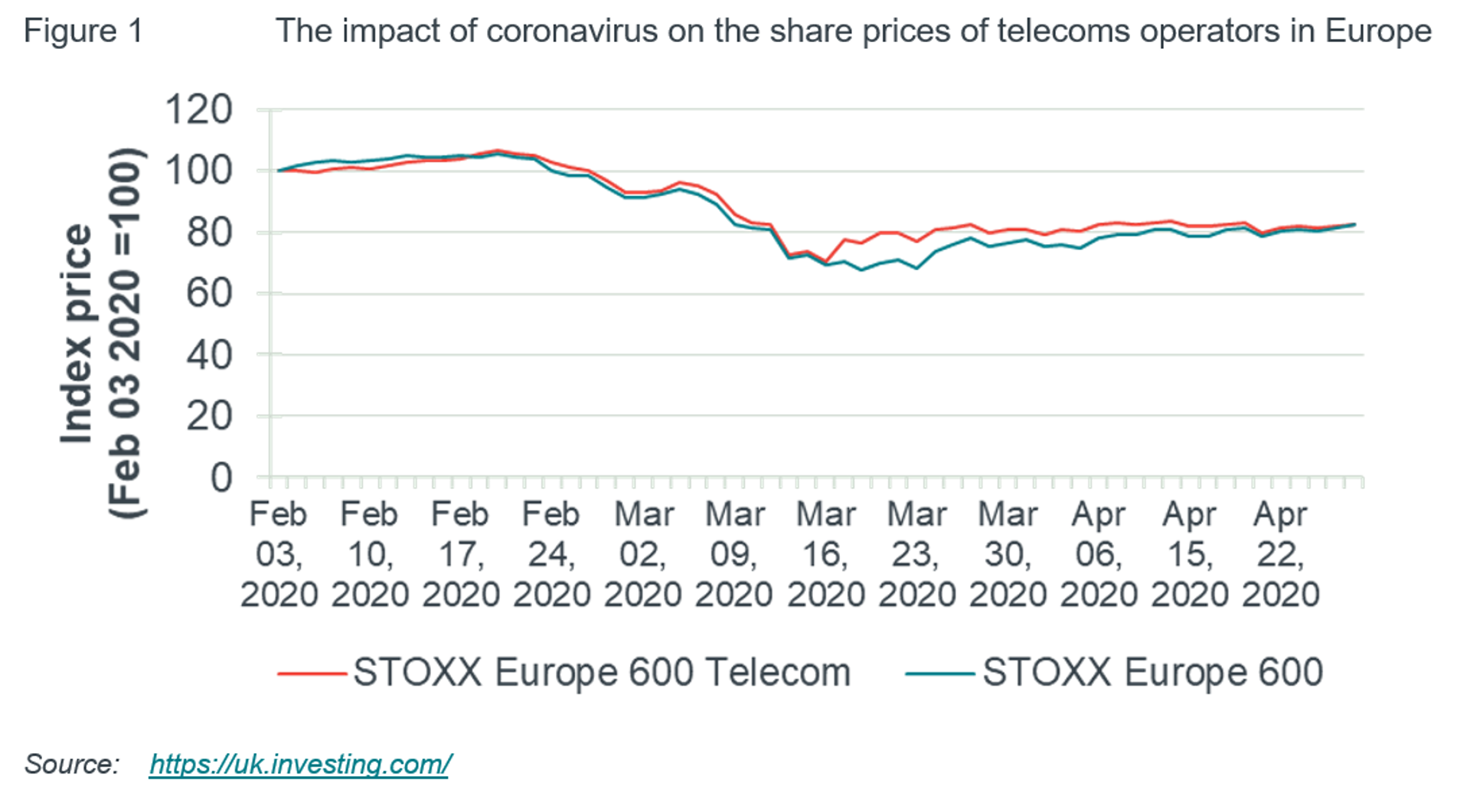
The sharp fall reflects the expectation, based on previous recessions, that reductions in income will sap demand for telecoms services. However, social distancing is increasing reliance on telecoms, which could partially offset the impact of the expected economic slump. While operators will be affected differently in the short run, according to, for example their customer mix, it is clear that telecoms networks are seeing a surge in network traffic over the lockdown. A key question for the sector, therefore, will be the extent to which a short term increase in demand for telecoms services can be maintained in the longer run and indeed, whether any such surge in usage can be monetised. As we set out in this paper, we believe there are reasons for at least some investors and telecoms operators to be cautiously optimistic.
A surge in network traffic - but will it last?
There is plenty of evidence that stringent social distancing measures have led to a surge in overall demand for telecoms services, especially on fixed networks. For example, Telecom Italia CEO Luigi Gubitosi has said there has been a 70% increase in internet traffic over its fixed network, partly thanks to video streaming and gaming applications. Similarly, Vodafone has reported an increase in fixed broadband traffic of over 50% in Spain and Italy, alongside a 30% rise in mobile data traffic. Indeed, BEREC, the representative body for European telecoms regulators, confirms that “overall traffic on fixed and on mobile networks has increased during the Covid-19 crisis”. However, in some cases data usage on mobile networks is bucking this trend. For example, BT has recorded a 5% fall in mobile data traffic, explained by increased offload of mobile traffic to fixed networks due to people spending more time at home.

What might this mean for telecoms operators?
In the short term…
While stringent social distancing measures are putting a significant strain on the economy as a whole, it is not clear that this will translate into a material reduction in telecom operator revenues. Given the central role of telecoms in softening the impact of social distancing on both businesses and households, most consumers will want to keep their services where possible. This may make telecoms revenues less sensitive to a fall in GDP than in other recessions.
But, more usage may not mean higher revenues…
At the same time, it is unlikely that the increase in overall usage across fixed and mobile networks will translate into higher operator revenues, at least in the short term, given that, particularly in the EU:
- Most households will already be on ‘unlimited’ packages for fixed services.
- While mobile plans (in contrast to fixed) typically have a cap on data usage, subscribers have the option of switching to their home WiFi network when they hit their limit rather than upgrading to a more expensive package.
- Operators in many countries have substantially increased customer allowances and fixed broadband speeds temporarily in response to the virus.
- Telecoms operators will be under pressure to support subscribers who may be unable, in the short term, to pay their bills.
…while the lockdown will put pressure on certain revenue streams
Strict travel curbs mean roaming has fallen sharply. For example, Vodafone New Zealand has reported a staggering 99% drop in international roaming traffic And it is unlikely to be alone. This will impact operators differently. In Europe, for instance, returns from roaming have declined sharply over the last decade, since the introduction of the ‘roam like at home’ regulation, which treated roaming largely the same as domestic traffic. However, even within Europe, operators in some countries are likely to be more adversely affected than others, while outside Europe, those operators based in tourist hotspots or business hubs are likely to suffer more markedly.
Mobile operators may not be alone in facing some declines in revenues, however. In particular, there could also be some hit to revenues from business services if most people are working from home and firms are under pressure to cut costs. While many companies will be locked into contracts, if nothing else coronavirus may dampen operators’ hopes of selling more services, e.g. IT and IoT, especially to SMEs, in the short term. Further, revenues will clearly suffer if businesses shut down entirely (either temporarily or permanently).
Less switching could actually lead to a softening in competition in the short term, with this having different impacts on operators
The crisis could lead to less switching between operators in the short term, partly because operators in many countries have closed their bricks-and-mortar stores while supply chain disruptions have delayed the launch of many new smartphones. Moreover, fewer network engineers and customer support staff are available during the crisis. There may also be a general reluctance to switch providers during lockdown, either for fear of temporarily losing service or simply because it is not a current priority. Temporary increases in customer allowances introduced by several operators may also reduce churn rates by obviating the need to seek out a new deal.
There is already some evidence, from Italy, that switching has indeed plummeted as a result of the crisis: number porting has fallen by around two-thirds. In China, device sales fell by around 30% over the course of January and February. The impact of a reduction in switching will vary depending on operators’ market position – lower churn rates are likely to hit more recent entrants that have been expanding rapidly. On the other hand, established players that have been losing customers could benefit in the short term. How customers may behave once lockdowns are lifted is less clear. On the one hand, cash-strapped consumers and businesses may be more willing to switch in order to get a better deal, as they will be looking to cut costs wherever possible, thus potentially benefitting those providers who focus on offering low cost deals to consumers. In contrast, however, there may also be a flight to higher quality services, with consumers being less willing to put up with intermittent services or coverage gaps.
…. and in the longer term
Given the potential duration of the crisis and the expectation that society will need to adjust to a “new normal”, a number of the effects outlined above may prevail for a considerable period of time. Beyond this, the extent to which the crisis will impact on the telecoms sector in the medium to longer term, once travel restrictions and social distancing measures have been eased, is unclear. Unlike in previous recessions however, the overall impact on operator revenues will hinge on two countervailing factors:
- A negative effect from lower GDP. The ‘standard’ impact from the economic slowdown will depend on the depth and length of the economic recession, and the extent to which unemployment rises. The jury is still out on how severe the recession will be, but most commentators seem to be expecting a sharp reduction in GDP in 2020 followed by a rebound in 2021. For example, the IMF has forecast that GDP in advanced economies will fall by 6.1% in 2020 followed by a 4.5% rebound in 2021. The conventional view is that demand for telecoms services over an economic cycle is proportional to GDP – so under a normal recession a GDP reduction of -1% would reduce telecoms sector revenues by -1%.
- A positive effect from greater reliance on telecoms services. It is possible that the pandemic could foster a long term shift towards greater reliance on telecoms services, which could in turn help offset the downwards pressure on operator revenues due to lower GDP. For example, it is quite plausible that there will be a sustained increase in remote working, the use of streaming services, remote healthcare, distance learning, video calls and so on. This is mainly likely to increase demand for fixed broadband services, but could also have some positive impact on the demand for mobile services, for instance as a result of consumers becoming more familiar with using certain apps during the lockdown. For example, if one assumed that the demand for fixed broadband usage increased by 10%-20% over the longer term as a result of households having become more accustomed to using such services during the lockdown period (relative to the 50% increase seen in many countries during the lockdown itself), and as a result 10%-20% of subscribers on standard fixed broadband connections decided to upgrade to a superfast broadband connection (above 30Mbps as defined by Ofcom), then this could result in a 0.5%-1% uplift in total telecoms revenues. Telecoms networks are configured to deal with peaks in traffic, which typically occur during the evening. As most of the increased usage would occur during off-peak hours (assuming some element of “lockdown” working and leisure patterns are maintained post-lockdown) and the coverage of broadband networks above 30Mbps is already high in many markets (83% in the EU, for instance), operators may be able to meet this demand with minimal additional investments. This means that the higher revenues should feed through into the bottom line.
Given this, it could be reasonable to expect the sector to bounce back more quickly than has been the case from previous economic downturns. Indeed, the recognised importance of telecoms to keeping us all connected during the lockdown, as well as driving longer term changes in usage, may also reignite debates about the role of the sector in today’s economy and policy measures that can promote the uptake of high speed connectivity. This could represent a further opportunity to telecoms operators, though with government finances also reeling from the impact of coronavirus, it is unclear to what extent further government support may be available.






